The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 110, 109147, 2022
Friday, 30 September 2022
Crosstalk between xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibiting and cancer chemotherapeutic properties of comestible flavonoids- a comprehensive update
Monday, 26 September 2022
Biological Functions and Utilization of Different Part of the Papaya: A Review
Papaya is one of the most important fruit trees cultivated throughout the tropical and subtropical regions and its production is rising worldwide. Its edible part has a high nutritional and sensory value and a great commercial potential. Mature papaya is consumed fresh and has been used in food processing and cosmetic industries. Along with some other parts such as leaves, seeds or skin, papaya has been used in traditional medicine in various countries. In fact, numerous studies have reported the presence of bioactive compounds with diverse biological properties in the papaya by-products, which has motivated the expansion of their applications. Papaya by-products have been demonstrated to exert a wide range of activities (e.g.; antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-dengue, anti-malarial, anti-fertility, diabetes prevention, insecticidal, anti-AIDS) that could be useful in pharmaceutical industry. They could be used in food industry, as a source of functional compounds and in innovative active packaging strategies, and in different cosmetic products, among other applications. Although this scenario indicates that the papaya industry could diversify and increase its economic value, there are two problems that significantly affect it: the spread of pathogens and the highly perishable nature of this fruit. On the one hand, genetic tools have been used to obtain transgenic varieties resistant to pathogens, while new preservation technologies have been explored. This review focuses on the main bioactive compounds, important physiological functions and applications of different papaya parts and also in the current development of genetically modified papaya in the industry and the research progress on storage and preservation.
Thursday, 22 September 2022
Polyphenols as possible alternative agents in chronic fatigue: a review
Friday, 16 September 2022
Enrichment of gamma-aminobutyric acid in foods: From conventional methods to innovative technologies
Food Res. Int. 162, Part A, 111801, 2022
Wednesday, 14 September 2022
Himalayan Wild Fruits as a Strong Source of Nutraceuticals, Therapeutics, Food and Nutrition Security
Tuesday, 13 September 2022
Single-Cell Proteins Obtained by Circular Economy Intended as a Feed Ingredient in Aquaculture
The constant increment in the world’s population leads to a parallel increase in the demand for food. This situation gives place the need for urgent development of alternative and sustainable resources to satisfy this nutritional requirement. Human nutrition is currently based on fisheries, which accounts for 50% of the fish production for human consumption, but also on agriculture, livestock, and aquaculture. Among them, aquaculture has been pointed out as a promising source of animal protein that can provide the population with high-quality protein food. This productive model has also gained attention due to its fast development. However, several aquaculture species require considerable amounts of fish protein to reach optimal growth rates, which represents its main drawback. Aquaculture needs to become sustainable using renewable source of nutrients with high contents of proteins to ensure properly fed animals. To achieve this goal, different approaches have been considered. In this sense, single-cell protein (SCP) products are a promising solution to replace fish protein from fishmeal. SCP flours based on microbes or algae biomass can be sustainably obtained. These microorganisms can be cultured by using residues supplied by other industries such as agriculture, food, or urban areas. Hence, the application of SCP for developing innovative fish meal offers a double solution by reducing the management of residues and by providing a sustainable source of proteins to aquaculture. However, the use of SCP as aquaculture feed also has some limitations, such as problems of digestibility, presence of toxins, or difficulty to scale-up the production process. In this work, we review the potential sources of SCP, their respective production processes, and their implementation in circular economy strategies, through the revalorization and exploitation of different residues for aquaculture feeding purposes. The data analyzed show the positive effects of SCP inclusion in diets and point to SCP meals as a sustainable feed system. However, new processes need to be exploited to improve yield. In that direction, the circular economy is a potential alternative to produce SCP at any time of the year and from various cost-free substrates, almost without a negative impact.
Wednesday, 31 August 2022
Pirfenidone and post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis: invoked again for realistic goals
Inflammopharmacology, 30, 2017–2026 (2022)
Tuesday, 30 August 2022
Comparative study on the phenolic composition and in vitro bioactivity of medicinal and aromatic plants from the Lamiaceae family
Food Res. Int. 161, 111875, 2022
Thursday, 25 August 2022
The Nutritional and Bioactive Components, Potential Health Function and Comprehensive Utilization of Pomegranate: A Review
Tuesday, 23 August 2022
Hepatoprotective Mechanism of Ginsenoside Rg1 against Alcoholic Liver Damage Based on Gut Microbiota and Network Pharmacology
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 5025237
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a major public health problem worldwide, which needs to be effective prevention. Ginsenoside Rg1 (GRg1), a bioactive ingredient extracted from ginseng, has benefit effects on health. In this study, 11 potential targets of GRg1 against ALD were firstly obtained by network pharmacology. KEGG pathway enrichment showed that GRg1-target-ALD was closely related to Toll-like receptor (TLR) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathways. In addition, GRg1 decreased antioxidant levels and increased oxidative levels in alcohol-treated mice, which alleviated oxidative stress-induced hepatic damage. GRg1 enhanced intestinal barrier function via upregulating the levels of tight junction protein and immunoglobulin A. GRg1 also reduced alcohol-induced inflammation by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB pathway, which was consistent with the prediction of network targets. Moreover, GRg1 altered GM population, and Verrucomicrobia, Bacteroidetes, Akkermansia, Bacteroides, Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, and Alloprevotella played positive association with intestinal barrier indicators and negative correlation with hepatic inflammation biomarkers. The results suggest that GRg1 administration might be a promising strategy for protection of alcohol-induced liver damage.
Wednesday, 10 August 2022
Metabolomics approach reveals high energy diet improves the quality and enhances the flavor of black Tibetan sheep meat by altering the composition of rumen microbiota
Monday, 1 August 2022
Safer plant-based nanoparticles for combating antibiotic resistance in bacteria: A comprehensive review on its potential applications, recent advances, and future perspective
Science of the Total Environment, 821, 153472. 2022
Background
Antibiotic resistance is one of the current threats to human health, forcing the use of drugs that are more noxious, costlier, and with low efficiency. There are several causes behind antibiotic resistance, including over-prescription of antibiotics in both humans and livestock. In this scenario, researchers are shifting to new alternatives to fight back this concerning situation.
Scope and approach
Nanoparticles have emerged as new tools that can be used to combat deadly bacterial infections directly or indirectly to overcome antibiotic resistance. Although nanoparticles are being used in the pharmaceutical industry, there is a constant concern about their toxicity toward human health because of the involvement of well-known toxic chemicals (i.e., sodium/potassium borohydride) making their use very risky for eukaryotic cells.
Key findings and conclusions
Multiple nanoparticle-based approaches to counter bacterial infections, providing crucial insight into the design of elements that play critical roles in the creation of antimicrobial nanotherapeutic drugs, are currently underway. In this context, plant-based nanoparticles will be less toxic than many other forms, which constitute promising candidates to avoid widespread damage to the microbiome associated with current practices. This article aims to review the actual knowledge on plant-based nanoparticle products for antibiotic resistance and the possible replacement of antibiotics to treat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections.
Tuesday, 26 July 2022
Advances on Natural Abietane, Labdane and Clerodane Diterpenes as Anti-Cancer Agents: Sources and Mechanisms of Action
Tuesday, 12 July 2022
Essential oils nano-emulsion confers resistance against Penicillium digitatum in 'Newhall' navel orange by promoting phenylpropanoid metabolism
Industrial Crops and Products, 187(A), 115297, 2022
Friday, 8 July 2022
The influence of phytochemicals on cell heterogeneity in chronic inflammation-associated diseases: the prospects of single cell sequencing
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 108, 109091, 2022
Friday, 1 July 2022
Biological properties and potential of compounds extracted from red seaweeds
Macroalgae have been recently used for different applications in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industry since they do not compete for land and freshwater against other resources. Moreover, they have been highlighted as a potential source of bioactive compounds. Red algae (Rhodophyta) are the largest group of seaweeds, including around 6000 different species, thus it can be hypothesized that they are a potential source of bioactive compounds. Sulfated polysaccharides, mainly agar and carrageenans, are the most relevant and exploited compounds of red algae. Other potential molecules are essential fatty acids, phycobiliproteins, vitamins, minerals, and other secondary metabolites. All these compounds have been demonstrated to exert several biological activities, among which antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antimicrobial properties can be highlighted. Nevertheless, these properties need to be further tested on in vivo experiments and go in-depth in the study of the mechanism of action of the specific molecules and the understanding of the structure–activity relation. At last, the extraction technologies are essential for the correct isolation of the molecules, in a cost-effective way, to facilitate the scale-up of the processes and their further application by the industry. This manuscript is aimed at describing the fundamental composition of red algae and their most studied biological properties to pave the way to the utilization of this underused resource.
Wednesday, 29 June 2022
Fu Brick Tea Manages HFD/STZ-Induced Type 2 Diabetes by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Activating the IRS1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 27, 8274–8287
Monday, 27 June 2022
Application of Protein in Extrusion-Based 3D Food Printing: Current Status and Prospectus
Friday, 10 June 2022
Lobularia libyca: Phytochemical Profiling, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity Using In Vitro and In Silico Studies
Saturday, 4 June 2022
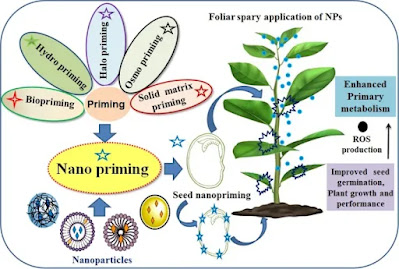
Nano-priming as emerging seed priming technology for sustainable agriculture—recent developments and future perspectives
Journal of Nanobiotechnology 20, 254 (2022)