Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 4472751
Thursday, 14 April 2022
Effects of Torreya grandis Kernel Oil on Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Flora in C57BL/6J Mice
Wednesday, 13 April 2022
Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from Paederia scandens (Lour.) Merr. Using deep eutectic solvent: optimization, identification, and comparison with traditional methods
Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 86, 106005, 2022
Ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE) coupled with deep eutectic solvent (DES) is a novel, efficient and green extraction method for phytochemicals. In this study, the effects of 16 DESs coupled with UAE on the extraction rate of polyphenols from Paederia scandens (Lour.) Merr. (P. scandens), an edible and medicinal herb, were investigated. DES synthesised with choline chloride and ethylene glycol at a 1:2 M ratio resulted in the highest extractability. Moreover, the effects of extraction parameters were investigated by using a two-level factorial experiment followed by response surface methodology The optimal parameters (water content in DES of 49.2%, the actual ultrasonic power of 72.4 W, and ultrasonic time of 9.7 min) resulted in the optimal total flavonoid content (TFC) (27.04 mg CE/g DW), ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) value (373.27 μmol Fe(Ⅱ)E/g DW) and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline)-6-sulfonic acid radical (ABTS+) value (48.64 μmol TE/g DW), closely matching the experimental results. Furthermore, a comparison study demonstrated that DES-UAE afforded the higher TFC and FRAP value than traditional extraction methods. 36 individual polyphenolic compounds were identified and quantified by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS) in P. scandens extracts, and of which 30 were found in the extracts obtained by DES-UAE. Additionally, DES-UAE afforded the highest sum of individual polyphenolic compound content. These results revealed that DES-UAE enhanced the extraction efficiency for polyphenols and provided a scientific basis for further processing and utilization of P. scandens.
Wednesday, 6 April 2022
Blockchain: An emerging novel technology to upgrade the current fresh fruit supply chain
Trends in Food Science & Technology, 124, 1-12, 2022
Wednesday, 23 March 2022
Anti-Depressant Properties of Crocin Molecules in Saffron
Tuesday, 15 March 2022
Natural Polyphenols for the Preservation of Meat and Dairy Products
Food spoilage makes foods undesirable and unacceptable for human use. The preservation of food is essential for human survival, and different techniques were initially used to limit the growth of spoiling microbes, e.g., drying, heating, salting, or fermentation. Water activity, temperature, redox potential, preservatives, and competitive microorganisms are the most important approaches used in the preservation of food products. Preservative agents are generally classified into antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-browning agents. On the other hand, artificial preservatives (sorbate, sulfite, or nitrite) may cause serious health hazards such as hypersensitivity, asthma, neurological damage, hyperactivity, and cancer. Thus, consumers prefer natural food preservatives to synthetic ones, as they are considered safer. Polyphenols have potential uses as biopreservatives in the food industry, because their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities can increase the storage life of food products. The antioxidant capacity of polyphenols is mainly due to the inhibition of free radical formation. Moreover, the antimicrobial activity of plants and herbs is mainly attributed to the presence of phenolic compounds. Thus, incorporation of botanical extracts rich in polyphenols in perishable foods can be considered since no pure polyphenolic compounds are authorized as food preservatives. However, individual polyphenols can be screened in this regard. In conclusion, this review highlights the use of phenolic compounds or botanical extracts rich in polyphenols as preservative agents with special reference to meat and dairy products.
Saturday, 12 March 2022
Ethnobotanical and phytochemical aspects of the edible herb Coriandrum sativum L.
Journal of Food Science, 87(4), 2022, 1386-1422
Friday, 4 March 2022
Unravelling the immunomodulatory role of apple phenolic rich extracts on human THP-1- derived macrophages using multiplatform metabolomics
Food Res. Int. 155, 111037, 2022
Thursday, 3 March 2022
Morus alba L. (Sangzhi) Alkaloids Promote Insulin Secretion, Restore Diabetic β-Cell Function by Preventing Dedifferentiation and Apoptosis
Front. Pharmacol., Sec. Ethnopharmacology, 2022
Tuesday, 1 March 2022
Simultaneous determination of ten nucleosides and bases in Ganoderma by micellar electrokinetic chromatography
Food Science and Human Wellness, 11 (2), 263-268, 2022
Thursday, 24 February 2022
Antidiabetic Phytochemicals From Medicinal Plants: Prospective Candidates for New Drug Discovery and Development
Friday, 18 February 2022
Extraction of the wheat straw hemicellulose fraction assisted by commercial endo-xylanases. Role of the accessory enzyme activities
Industrial Crops and Products, 179, 2022, 114655
Wheat straw is a highly promising raw material for bio-refinery strategies. Most of the literature related to lignocellulose fractionation focuses on cellulose purification and hemicellulose solubilization. Pre-treatments for hemicellulose solubilization without the formation of undesired products usually reach low extraction yields, which leaves an important hemicellulose fraction unused. In this work, we propose a mild process for the efficient extraction of the hemicellulose fraction of wheat straw assisted by partial enzymatic hydrolysis with three commercial endo-xylanase cocktails. A first step with alkali at 40 ºC helped to disrupt the lignocellulosic structure and removed 19% of lignin while maintaining most of the hemicellulose in the solid. The enzymatic step enabled reaching extraction yields of 59.8%, 51.9%, and 42.5% with Ultraflo L, Pentopan mono conc, and Shearzyme 500L, respectively. We also discuss the catalytic properties of each endo-xylanase, in particular, their adscription to the GH10 or GH11 glycosyl hydrolase family, and the relevant role of accessory enzymes.
Thursday, 17 February 2022
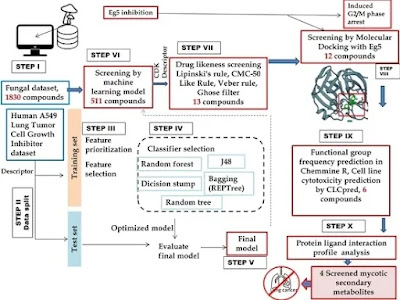
Integrated Machine Learning and Chemoinformatics-Based Screening of Mycotic Compounds against Kinesin Spindle ProteinEg5 for Lung Cancer Therapy
Among the various types of cancer, lung cancer is the second most-diagnosed cancer worldwide. The kinesin spindle protein, Eg5, is a vital protein behind bipolar mitotic spindle establishment and maintenance during mitosis. Eg5 has been reported to contribute to cancer cell migration and angiogenesis impairment and has no role in resting, non-dividing cells. Thus, it could be considered as a vital target against several cancers, such as renal cancer, lung cancer, urothelial carcinoma, prostate cancer, squamous cell carcinoma, etc. In recent years, fungal secondary metabolites from the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) have been identified as an important lead source in the drug development pipeline. Therefore, the present study aims to identify potential mycotic secondary metabolites against the Eg5 protein by applying integrated machine learning, chemoinformatics based in silico-screening methods and molecular dynamic simulation targeting lung cancer. Initially, a library of 1830 mycotic secondary metabolites was screened by a predictive machine-learning model developed based on the random forest algorithm with high sensitivity (1) and an ROC area of 0.99. Further, 319 out of 1830 compounds screened with active potential by the model were evaluated for their drug-likeness properties by applying four filters simultaneously, viz., Lipinski’s rule, CMC-50 like rule, Veber rule, and Ghose filter. A total of 13 compounds passed from all the above filters were considered for molecular docking, functional group analysis, and cell line cytotoxicity prediction. Finally, four hit mycotic secondary metabolites found in fungi from the IHR were screened viz., (−)-Cochlactone-A, Phelligridin C, Sterenin E, and Cyathusal A. All compounds have efficient binding potential with Eg5, containing functional groups like aromatic rings, rings, carboxylic acid esters, and carbonyl and with cell line cytotoxicity against lung cancer cell lines, namely, MCF-7, NCI-H226, NCI-H522, A549, and NCI H187. Further, the molecular dynamics simulation study confirms the docked complex rigidity and stability by exploring root mean square deviations, root mean square fluctuations, and radius of gyration analysis from 100 ns simulation trajectories. The screened compounds could be used further to develop effective drugs against lung and other types of cancer.
Wednesday, 16 February 2022
Evaluation and Mathematical Analysis of a Four-Dimensional Lotka–Volterra-like Equation Designed to Describe the Batch Nisin Production System
Nisin, an antibacterial compound produced by Lactococcus lactis strains, has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to be used as a safe food additive to control the growth of undesirable pathogenic bacteria. Nisin is commonly described as a pH-dependent primary metabolite since its production depends on growth and culture pH evolution. However, the relationships between bacteriocin synthesis (BT), biomass production (X), culture pH, and the consumption of the limiting nutrient (total nitrogen: TN) have not been described until now. Therefore, this study aims to develop a competitive four-dimensional Lotka–Volterra-like Equation (predator-prey system) to describe these complex relationships in three series of batch fermentations with L. lactis CECT 539 in diluted whey (DW)-based media. The developed four-dimensional predator-prey system accurately described each individual culture, providing a good description of the relationships between pH, TN, X, and BT, higher values for R2 and F-ratios, lower values (<10%) for the mean relative percentage deviation modulus, with bias and accuracy factor values approximately equal to one. The mathematical analysis of the developed equation showed the existence of one asymptotically stable equilibrium point, and the phase’s diagram obtained did not show the closed elliptic trajectories observed in biological predator-prey systems.
Tuesday, 15 February 2022
Thermochemical Characterization of Eight Seaweed Species and Evaluation of Their Potential Use as an Alternative for Biofuel Production and Source of Bioactive Compounds
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(4), 2355
Monday, 14 February 2022
Luteolin Alleviates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation Induced by Oxidative Injury in ARPE-19 Cell via Nrf2 and AKT/GSK-3β Pathway
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 2265725
Oxidative stress plays a critical role in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is involved in this process. The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effects of luteolin, a natural flavonoid with strong antioxidant activity, on H2O2-induced EMT in ARPE-19 cells. ARPE-19 cells were incubated with H2O2 at 200 μΜ to induce oxidative stress-associated injury. Cell viability assay showed that luteolin at 20 and 40 μM significantly promoted cell survival in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells. Luteolin also markedly protected ARPE-19 cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis. Cell migration assay presented that luteolin significantly reduced H2O2-induced migration in APRE-19 cells. EMT in ARPE-19 cells was detected by western blotting and immunofluorescence. The results showed that H2O2 significantly upregulated the expression of α-SMA and vimentin and downregulated the expression of ZO-1 and E-cadherin, while cells pretreated with luteolin showed a reversal. Meanwhile, the assessment of effects of luteolin on the Nrf2 pathway indicated that luteolin promoted Nrf2 nuclear translocation and upregulated the expressions of HO-1 and NQO-1. In addition, luteolin significantly increased the activities of SOD and GSH-PX and decreased intracellular levels of ROS and MDA in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells. Meanwhile, we observed that the expression of TGF-β2, p-AKT, and p-GSK-3β was upregulated in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells and downregulated in luteolin-treated cells, revealing that luteolin inhibited the activation of the AKT/GSK-3β pathway. However, these effects of luteolin were all annulled by transfecting ARPE-19 cells with Nrf2 siRNA. Our current data collectively indicated that inhibition of luteolin on EMT was induced by oxidative injury in ARPE-19 cell through the Nrf2 and AKT/GSK-3βpathway, suggesting that luteolin could be a potential drug for the treatment of dry AMD.
Friday, 4 February 2022
Development of nanofiber indicator with high sensitivity for pork preservation and freshness monitoring
A visual Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) fibrous film incorporated with Roselle anthocyanin (RS) and Cinnamon essential oil (CEO) (PRC film) was designed via electrospinning technology for pork preservation and freshness monitoring. The PRC film presented well structural integrity and stability in buffer solutions without leaking out RS. And PCR film had well hydrophobic and high permeability with water contact angle (WCA) of 109.52° and water vapor permeability (WVP) of 2.63 × 10−7 g m−1h−1Pa−1. Importantly, PRC film exhibited good antibacterial activity with the inhibition diameter at 29.0 mm and 27.1 mm which against Escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus, respectively. Finally, the PRC film was employed as a colorimetric sensor for monitoring pork freshness. It presented visible color changes from pink to blue and effectively prolonged the pork shelf-life by 2 days at 4 °C. These results indicate a great potential in intelligent and active packaging.
Thursday, 3 February 2022
Phytochemical and multi-biological characterization of two Cynara scolymus L. varieties: A glance into their potential large scale cultivation and valorization as bio-functional ingredients
Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 178, 114623
Artichoke leaf (Cynarae folium) extracts are used as traditional herbal medicinal products to treat a wide range of human ailments, being widely commercialized as nutraceutical or pharmaceutical preparations. In the current study, the hydromethanolic dried leaf extracts of Cynara scolymus L. var. major Brotero and C. scolymus L. var. redonensis N.H.F. Desp. were phytochemically and biologically investigated. The liquid chromatography high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS/MS) metabolite profiling showed a complex composition, with phenolic acids (mostly mono- and di-caffeoylquinic acids), flavonoids and sesquiterpene lactones as the most representative classes. The strong antioxidant activity of the two C. scolymus varieties was evidenced in DPPH [64.84–65.21 mg trolox equivalents (TE)/g] and ABTS (86.39–95.55 mg TE/g) radical scavenging, cupric (160.49–171.07 mg TE/g) and ferric (71.47–78.95 mg TE/g) reducing capacity, metal chelating and phosphomolybdenum assays. In addition, the two extracts also displayed anti-enzymatic effects, as assessed in cholinesterase, tyrosinase, glucosidase and amylase tests. Lastly, the artichoke samples (at the concentration of 20 μg/mL) proved a very potent inhibition of the production of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, namely interleukin (IL)-1β [7.55–15.75% of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) + cells], IL-8 (11.72–13.46% of LPS + cells) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (4.07–10.35% LPS + cells), in LPS-stimulated human neutrophils. Overall, the results of our study indicate that the two C. scolymus varieties could be regarded as a rich source of biologically active compounds, opening thus the perspectives for their future large scale cultivation and valorization as bio-functional ingredients with putative antioxidant, anti-enzymatic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Wednesday, 2 February 2022
Effect of Silymarin as an Adjunct Therapy in Combination with Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin in Hepatitis C Patients: A Miniature Clinical Trial
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 9199190
Silymarin is proclaimed to be a blend of flavonolignans or phytochemicals. An era of new generation of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) has commenced to have facet effect in swaying of the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Nonetheless, this therapy has serious side effects that jeopardize its efficacy. This study is aimed at probing the effects of ribavirin (RBV) and sofosbuvir (SOF) along with silymarin as an adjunct therapy on hematological parameters and markers of obscured oxidative stress. The effect of DAAs along with silymarin was also examined on variable sex hormone level and liver function markers such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and bilirubin. The study was followed to determine viral load and viral genotypes. A total of 30 patients were randomly divided into two equal groups comprising the control group () and treatment group (). The control group was solely administered with DAAs (SOF and RBV; 400 mg/800 mg each/day). Conversely, the treatment group was dispensed with DAAs, but with adjunct therapy of silymarin (400 mg/day) along with DAAs (400/800 mg/day) over period of 8 weeks. Sampling of blood was performed at pre- and posttreatment levels for the evaluation of different propound parameters. Our data showed that silymarin adjunct therapy enhances the efficiency of DAAs. A decrease in menace level of liver markers such as ALT, ALP, AST, and bilirubin was observed (). The adjunct therapy concurrently also demonstrated an ameliorative effect on hematological indices and oxidative markers, for instance, SOD, TAS, GSH, GSSG, and MDA (), diminishing latent viral load. The silymarin administration was also found to revamp the fluster level of sex hormones. Our outcomes provide evidence that systematic administration of silymarin effectively remits deviant levels of hematological, serological, hormonal, and antioxidant markers. This demonstrates a possibly unique role of silymarin in mitigating hepatitis C.
Tuesday, 1 February 2022
Agar/TiO2/radish anthocyanin/neem essential oil bionanocomposite bilayer films with improved bioactive capability and electrochemical writing property for banana preservation
Food Hydrocolloids 123, 107187, 2022
Active agar (AG) bilayer films with bioactive capability and electrochemical writing property were developed for improving the postharvest quality of the banana. The antioxidant and antimicrobial capacity of the films were enhanced with the incorporation of red radish extract (RRE) and neem essential oil (NEO) into AG lower layer. The barrier and mechanical properties, retention of total anthocyanin and NEO content in the bilayer films were effectively improved with addition of TiO2 into the AG upper layer. Multicolor patterns were successfully written on the bilayer film containing RRE. The AG-TiO2+AG-RRE-NEO bilayer film exhibited the optimal preservations on banana fruits during the storage period, based on the characterization by fruits appearance, senescent spotting symptom, microbial analysis, weight loss and firmness. Thus, the AG-TiO2+AG-RRE-NEO bilayer film was expected to be a multifunction packaging material for banana preservation.
Monday, 31 January 2022
Pigment Composition of Nine Brown Algae from the Iberian Northwestern Coastline: Influence of the Extraction Solvent
Brown algae are ubiquitously distributed in the NW coastline of the Iberian Peninsula, where they stand as an underexploited resource. In this study, five solvents were applied to the extraction of pigments from nine brown algae, followed by their determination and quantification by HPLC-DAD. A total of 13 compounds were detected: Six were identified as chlorophylls, six were classified as xanthophylls, and one compound was reported as a carotene. Fucoxanthin was reported in all extracts, which is the most prominent pigment of these algae. Among them, L. saccharina and U. pinnatifida present the highest concentration of fucoxanthin (4.5–4.7 mg∙g−1 dry weight). Ethanol and acetone were revealed as the most efficient solvents for the extraction of pigments, showing a maximal value of 11.9 mg of total pigments per gram of dry alga obtained from the ethanolic extracts of H. elongata, followed by the acetonic extracts of L. ochroleuca. Indeed, ethanol was also revealed as the most efficient solvent according to its high extraction yield along all species evaluated. Our results supply insights into the pigment composition of brown algae, opening new perspectives on their commercial exploitation by food, pharmaceutical, and cosmeceutical industries.
Monday, 24 January 2022
Polyphenols: A first evidence in the synergism and bioactivities
Tuesday, 18 January 2022
A dual-signal fluorescent sensor based on MoS2 and CdTe quantum dots for tetracycline detection in milk
Monday, 17 January 2022
Chitosan and flavonoid glycosides are promising combination partners for enhanced inhibition of heterocyclic amine formation in roast beef
Food Chemistry, 375, 131859, 2022
Sunday, 16 January 2022
Development, characterization and stability of a white cachama pâté-type product (Piaractus brachypomus)
Saturday, 15 January 2022
Effects of different feeding regimes on muscle metabolism and its association with meat quality of Tibetan sheep
Friday, 14 January 2022
Impact of chiral tebuconazole on the flavor components and color attributes of Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon wines at the enantiomeric level
Food Chem. 373, Part B, 131577, 2022
Thursday, 13 January 2022
Freezing characteristics and relative permittivity of rice flour gel in pulsed electric field assisted freezing
Food Chem. 373, Part A, 131449, 2022
Wednesday, 12 January 2022
Cellular antioxidant potential and inhibition of foodborne pathogens by a sesquiterpene ilimaquinone in cold storaged ground chicken and under temperature-abuse condition
Food Chem. 373, Part A, 131392, 2022
A sesquiterpene quinone, ilimaquinone, was accessed for its cellular antioxidant efficacy and possible antimicrobial mechanism of action against foodborne pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli) in vitro and in vivo. Ilimaquinone was found to be protective against H2O2-induced oxidative stress as validated by the reduction in the ROS levels, including increasing expression of SOD1 and SOD2 enzymes. Furthermore, ilimaquinone evoked MIC against S. aureus and E. coli within the range of 125–250 µg/mL. Ilimaquinone established its antimicrobial mode of action against both tested pathogens as evident by bacterial membrane depolarization, loss of nuclear genetic material, potassium ion, and release of extracellular ATP, as well as compromised membrane permeabilization and cellular component damage. Also, ilimaquinone showed no teratogenic effect against zebrafish, suggesting its nontoxic nature. Moreover, ilimaquinone significantly reduced the S. aureus count without affecting the sensory properties and color values of cold-storaged ground chicken meat even under temperature abuse condition.
Tuesday, 11 January 2022
Stability and antioxidant capacity of epigallocatechin gallate in Dulbecco's modified eagle medium
Monday, 10 January 2022
Assessment of the Ecological Risk from Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediment of River Surma, Bangladesh: Coupled Approach of Monte Carlo Simulation and Multi-Component Statistical Analysis
River sediment can be used to measure the pollution level in natural water, as it serves as one of the vital environmental indicators. This study aims to assess heavy metal pollution namely Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Zinc (Zn), Nickel (Ni), Lead (Pb), and Cadmium (Cd) in Surma River. Further, it compares potential ecological risk index values using Hakanson Risk Index (RI) and Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS) approach to evaluate the environmental risks caused by these heavy metals. in the study area. With obtained results, enrichment of individual heavy metals in the study area was found in the order of Ni > Pb > Cd > Mn > Cu > Zn. Also, variance in MCS index contributed by studied metals was in the order of Cd > Pb > Ni > Zn > Cu. None of the heavy metals, except Ni, showed moderate contamination of the sediment. Risk index values from RI and MCS provide valuable insights in the contamination profile of the river, indicating the studied river is currently under low ecological risk for the studied heavy metals. This study can be utilized to assess the susceptibility of the river sediment to heavy metal pollution near an urban core, and to have a better understanding of the contamination profile of a river.
Sunday, 9 January 2022
Valorization of kiwi agricultural waste and industry by-products by recovering bioactive compounds and applications as food additives: A circular economy model
Saturday, 8 January 2022
Weed pressure determines the chemical profile of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and its allelochemicals potential
Pest Management Science, 78, 1605-1619, 2022
BACKGROUND
Common purslane (Portulaca oleracea) and annual ryegrass (Lolium rigidum) are important infesting weeds of field crops. Herbicides are mostly used for weed suppression, while their environmental toxicity and resistance in weeds against them demand considering alternative options, such as the use of allelopathic crops for weed management. Wheat is an important allelopathic crop and present research focused on the identification and quantification of benzoxazinoids (BXZs) and polyphenols (phenolic acids and flavonoids) of the wheat accession ‘Ursita’ and to screen its allelopathic impact on P. oleracea and Lolium rigidum through equal-compartment-agar (ECA) method.
RESULTS
Weed germination, radicle length, biomass and photosynthetic pigments were altered following co-growth of weeds with Ursita for 10-day. Root exudates from Ursita reduced (29–60%) the seedling growth and photosynthetic pigments of Lolium rigidum depending on co-culture conditions of planting density. Weed pressure caused significant increase in the production of phenolic acids (vanillic, ferulic, syringic and p-coumaric acids) and root exudation of BXZs, in particular benzoxazolin-2-one (BOA), 2-hydroxy-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one (HMBOA), 2-hydroxy-1,4-benzoxazin3-one (HBOA) and 2,4-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one (DIBOA) in wheat tissues (shoots, roots) and exudate in root rhizosphere agar medium in response to co-cultivation with Lolium rigidum and P. oleracea, depending on weed/crop density.
CONCLUSION
The work revealed that Ursita is allelopathic in nature and can be used in breeding programs to enhance its allelopathic activity. Meanwhile, there are opportunities to explore allelopathic effect of wheat cultivars to control P. oleracea and Lolium rigidum under field conditions. © 2022 The Authors. Pest Management Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society of Chemical Industry.
Friday, 7 January 2022
Effects of Polyphenols on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Interconnected Pathways during Spinal Cord Injury
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 8100195
Thursday, 6 January 2022
Benefits, toxicity and current market of cannabidiol in edibles
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
The commercialization of products with cannabidiol (CBD) has undergone a significant increase. These products can be presented in different forms such as baked goods, gummies or beverages (such as kombucha, beer or teas, among others) using wide concentrations ranges. The use of CBD in edibles favors its consumption, for medicinal users, during the work week, avoid its possible social stigma and facilitates its transport. These products can be purchased on store shelves and online. There is a large number of specialized studies, in which the possible advantages of CBD consumption are described in the preclinical and clinical trials. It is also necessary to recognize the existence of other works revealing that the excessive consumption of CBD could have some repercussions on health. In this review, it is analyzed the composition and properties of Cannabis sativa L., the health benefits of cannabinoids (focusing on CBD), its consumption, its possible toxicological effects, a brief exposition of the extraction process, and a collection of different products that contain CBD in its composition.
Wednesday, 5 January 2022
Coffee silverskin: Characterization of B-vitamins, macronutrients, minerals and phytosterols
The present study assessed the nutritional composition of coffee silverskin (CSS) obtained from arabica roasted coffee. Following validated analytical methods, CSS resulted to be a high source of proteins (14.2 g/100 g) and dietary fibers (51.5 g/100 g). Moreover, the mineral analysis revealed high contents of calcium (1.1 g/100 g) and potassium (1.0 g/100 g). To date, this study provided the widest mineral profile of CSS with 30 minerals targeted including 23 microminerals with high levels of iron (238.0 mg/kg), manganese (46.7 mg/kg), copper (37.9 mg/kg), and zinc (31.9 mg/kg). Moreover, vitamins B2 (0.18–0.2 mg/kg) and B3 (2.5–3.1 mg/kg) were studied and reported for the first time in CSS. β-sitosterol (77.1 mg/kg), campesterol, stigmasterol, and Δ5-avenasterol, were also observed from the phytosterol analysis of CSS with a total level of 98.4 mg/kg. This rich nutritional profile highlights the potential values of CSS for innovative reuses in bioactive ingredients development.