Trends Food Sci. Technol. 134, 29-40 (2023)
Tuesday 28 February 2023
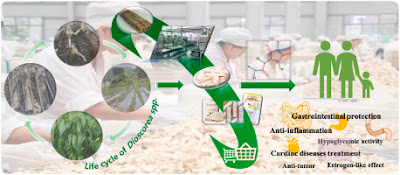
Chinese yam (Dioscorea): Nutritional value, beneficial effects, and food and pharmaceutical applications
Monday 27 February 2023
Green preparation of bract extract (Musa acuminate) doped magnesium oxide nanoparticles and their bioefficacy
App. Org. Chem. 37 (5), e7063 (2023)
Sunday 26 February 2023
Bioactive Compounds of Verbascum sinuatum L.: Health Benefits and Potential as New Ingredients for Industrial Applications
Saturday 25 February 2023
A visual bi-layer sensor based on Agar/TiO2/butterfly bean flower anthocyanin/κ-carrageenan with photostability for monitoring Penaeus chinensis freshness
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 235, 123706 (2023)
Wednesday 22 February 2023
Plant Alkaloids: Production, Extraction, and Potential Therapeutic Properties
Natural Secondary Metabolites. Springer, Cham. (2023)
Sulfur-Containing Compounds from Plants
Natural Secondary Metabolites. Springer, Cham. (2023)
Tuesday 21 February 2023
Health-Promoting Properties and Potential Application in the Food Industry of Citrus medica L. and Citrus × clementina Hort. Ex Tan. Essential Oils and Their Main Constituents
Citrus is an important genus in the Rutaceae family, with high medicinal and economic value, and includes important crops such as lemons, orange, grapefruits, limes, etc. The Citrus species is rich sources of carbohydrates, vitamins, dietary fibre, and phytochemicals, mainly including limonoids, flavonoids, terpenes, and carotenoids. Citrus essential oils (EOs) consist of several biologically active compounds mainly belonging to the monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes classes. These compounds have demonstrated several health-promoting properties such as antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Citrus EOs are obtained mainly from peels, but also from leaves and flowers, and are widely used as flavouring ingredients in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products. This review focused on the composition and biological properties of the EOs of Citrus medica L. and Citrus clementina Hort. Ex Tan and their main constituents, limonene, γ-terpinene, myrcene, linalool, and sabinene. The potential applications in the food industry have been also described.
Monday 20 February 2023
Research advance of non-thermal processing technologies on ovalbumin properties: The gelation, foaming, emulsification, allergenicity, immunoregulation and its delivery system application
Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nut. 2023
Sunday 19 February 2023
Dietary Protective Potential of Fucoxanthin as an Active Food Component on Neurological Disorders
J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8, 3599–3619
Saturday 18 February 2023
The roles of exogenous ATP in postharvest fruit and vegetable: A systematic meta-analysis
Postharvest Biology and Technology (2023) 199, 112305
Extracellular ATP (eATP) as an essential biological substance can trigger a series of physiological activities in postharvest fruit and vegetable during storage. We performed a systematic meta-analysis to elucidate better the multiple roles of exogenous ATP on the quality maintenance of postharvest fruit and vegetable during storage using a standard mean difference (SMD) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) and a random-effects model. This study determined 25 major indices of physiological activities of postharvest fruit and vegetable according to inclusion criteria. In forest plots, ATP application retarded the senescence (SMD −3.69, 95% CI [−5.32, −2.06]; I2 =100%; p = 0), maintained the nutritive quality (SMD 3.78, 95% CI [1.96, −5.63]; I2 = 100%; p = 0), contributed to high energy charge (SMD 1.99, 95% CI [−0.67, 4.66]; I2 = 100%; p = 0), attenuated membrane oxidant damage (SMD −4.08, 95% CI [−5.98, −2.18]; I2 = 100%; p = 0), and enhanced the antioxidant capacity (SMD 4.37, 95% CI [2.58, 6.15]; I2 = 100%; p = 0) of postharvest fruit and vegetable during storage. In conclusion, the results shed insights into the positive role of exogenous ATP in maintaining the quality of postharvest fruit and vegetable during storage via these physiological activities.
Thursday 16 February 2023
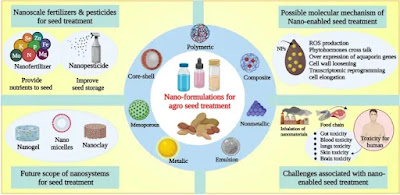
Recent Advances in Nano-Enabled Seed Treatment Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture: Challenges, Risk Assessment, and Future Perspectives
Nano-Micro Letters, 15, 54 (2023)
Wednesday 15 February 2023
Arctium lappa (Burdock): Insights from ethnopharmacology potential, chemical constituents, clinical studies, pharmacological utility and nanomedicine
Biomed. Pharm. 158, 114104, 2023
Wednesday 8 February 2023
Hypoglycaemic effect of total alkaloids extracted from Sambucus wightiana Wall. ex Wight & Arn. in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats
South African J Bot. 154, 330-355, 2023
Tuesday 7 February 2023
Increasing the shelf life of fresh in-hull pistachio using nanocomposite packaging of zinc nanoparticles and pistachio green hull essential oil
Monday 6 February 2023
La importancia de la acuicultura en la dieta saludable
Edible insects: Tendency or necessity
Sunday 5 February 2023
An intrinsic dual-emitting fluorescence sensing toward tetracycline with self-calibration model based on luminescent lanthanide-functionalized metal-organic frameworks
Saturday 4 February 2023
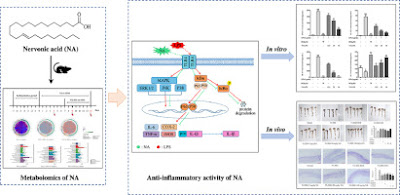
Improved colonic inflammation by nervonic acid via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway of DSS-induced colitis mice
Friday 3 February 2023
Metabolic profiling of Ochradenus baccatus Delile. utilizing UHPLC-HRESIMS in relation to the in vitro biological investigations
Thursday 2 February 2023
Mechanistic insights of Cucumis melo L. seeds for gastrointestinal muscle spasms through calcium signaling pathway–related gene regulation networks in WGCNA and in vitro, in vivo studies
Wednesday 1 February 2023
A review of recent innovative strategies for controlling mycotoxins in foods
Food Control, 144, 109350, 2023